| Medically reviewed by
Robin Backlund, BHSc
Last update:

Monitoring your heart health has never been more convenient, thanks to blood pressure monitors, also known as sphygmomanometers.
These invaluable devices utilize inflatable cuffs and manometers, which can be either mercury or aneroid, to provide precise blood pressure measurements.
Their ingenious design ensures controlled pressure release from the artery under the cuff, enabling accurate tracking of blood pressure levels during various activities and moments of rest.
Why should you consider owning a blood pressure monitor? Well, it’s not just about having a gadget; it’s about taking control of your health.
Regular self-monitoring can be a powerful motivator for making positive lifestyle changes, including adjustments to your diet and exercise routine.
Moreover, it has the potential to reduce healthcare costs by reducing the need for frequent medical visits.
For instance, a meta-analysis published in BMC Health Services Research by a team of scientists from City University London observed that cardiovascular patients who practiced proper self-monitoring experienced a 27% reduced risk of hospitalization.
There are several types of blood pressure monitors, but there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. These monitors come in various forms, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
For example, upper arm monitors, with their inflatable cuffs gently squeezing the arm to measure blood flow changes, are widely recognized for their accuracy.
Conversely, wrist and finger monitors cater to those with larger arms who may find upper arm cuffs uncomfortable, although they might compromise a bit on reliability in return.
Accuracy is paramount, so it’s advisable to cross-check your monitor annually against readings obtained at a healthcare provider’s office to ensure precision.
Upper-arm monitors are often the preferred choice for at-home use. In this context, below listed are some of the best blood pressure monitors currently available in the market.
- Oxiline Pressure X Pro
- Homedics Model: BPA-O300
- Checkme BP2A
- QardioArm
- Oxiline Pressure 9 Pro
- iHealth Track
- Omron HEM 6161
- Withings BPM Connect
- Omron Evolv
When selecting a monitor, one factor takes precedence: cuff size. An ill-fitting cuff can compromise the accuracy of your measurements.
Furthermore, ensure that the display is wide and clear so you won’t have a hard time understanding the readings. Also, consider the cost, which can vary depending on the brand, features, and monitor type (upper arm, wrist, or finger).
To make an informed purchase, you need the right source. The options are diverse, ranging from pharmacies and medical supply stores to online retailers and big-box stores, each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
Keep an eye out for ease of warranty settlement when making your purchase decision.
As for pricing, the range of BP monitors is broad, influenced by factors such as brand, features, and monitor type.
Also, don’t forget to check with your health insurance provider; they might cover the cost of a home blood pressure monitor.
To assist you further, we have included an extensive list of some of the best blood pressure monitors based on their functionality aspects.
Contents

1. Oxiline Pressure X Pro – Best overall
Features
- Vibra™ TX sensor
- FDA cleared accuracy
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity
- Specialized LED result screening
- App support for Android and iOS
The Oxiline Pressure X Pro, a remarkable product by Oxiline LLC, a medical device company located in Florida, USA, has made a significant impact in the blood pressure monitor market.
Oxiline LLC is renowned for creating products that greatly enhance individual health and lifestyle quality.
This smart blood pressure monitor boasts advanced technology, including cutting-edge nanosensors that deliver precise and in-depth blood pressure measurements. FDA clearance ensures accuracy and contributes to individual health support.
Its standout feature is its wireless connectivity, allowing effortless pairing with smartphones through Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, coupled with specialized result display on an LED screen.
Users have embraced the Oxiline Pressure X Pro for its portability and user-friendliness, making it an ideal choice for both home and on-the-go blood pressure monitoring.
Its simplicity and top-notch manufacturing have garnered widespread acclaim, cementing its reputation as a trusted companion for comfortable and reliable blood pressure monitoring.
PROS
- Accurate and reliable readings.
- Easy to use with clear instructions.
- Compact and portable design.
- Supports multiple users.
- Extended battery life.
- Comprehensive app features.
- Lifetime warranty, 30-day money-back guarantee.
CONS
- Higher price than some competitors.
- Requires regular calibration.
- Limited color options.
SPECIAL OFFER – 10% OFF
This is for TheEMTSpot’s readers only! Use code: EMTSPOT10 at the checkout to get 10% DISCOUNT.

2. Homedics Model: BPA-O300 – Best budget-friendly
Features
- Smart Measure® Inflation Technology
- Irregular heartbeat detector
- Excessive body motion detector
- Memory for 60 readings
- Easy-to-Read display
Homedics, established in 1987 in Detroit, has been a leading brand in wellness and home health innovations for over 30 years.
With its sleek and modern design, it has become a go-to choice for many online shoppers, thanks to its budget-friendly price tag.
The Homedics BPA-O300 is designed for quick, comfortable, and accurate blood pressure monitoring.
It features one-touch operation and Smart Measure® inflation technology, providing a personalized and precise measurement.
The monitor is also equipped with an irregular heartbeat detector and an excessive body motion detector, comparing readings to levels established by the American Heart Association (AHA 2017).
The product has generally received positive feedback, with users appreciating its ease of use and reliable readings.
PROS
- Accurate and reliable readings.
- Easy one-touch operation.
- The device can store 60 readings for a single user.
- Risk Category Index for easy comparison of readings.
- Comes with a five-year limited warranty.
- Available for purchase online and in retail stores like Walmart.
CONS
- Availability outside of the US is very limited.
Try Homedics BPA-O300 Today

3. CheckMe BP2 – Best for travel
Features
- Accurate integrated readings
- BP and ECG measurement
- In-built storage for 50 readings
- Portable one-button operation
- OLED display for clear visibility
The CheckMe BP2 blood pressure monitor is a Shenzhen Viatom Innovation Technology Co. Ltd product based in Shenzhen, China.
This device is noteworthy for accurately measuring blood pressure, even in individuals with irregular heart rates.
It combines readings taken at different times to provide the most reliable results. Moreover, it holds FDA clearance, ensuring consistent and dependable outcomes.
The BP2 serves as a blood pressure monitor and offers electrocardiographical outcomes (ECG), a feature uncommon in similar products.
With the capacity to store up to 50 readings in its memory, it aids users in tracking their blood pressure fluctuations. The device is highly portable and user-friendly for effortless operation.
In general, the CheckMe BP2 is hailed as one of the most technologically advanced blood pressure monitors available. Its lightweight and portable design, along with its USB rechargeability, contribute to its convenience.
PROS
- FDA-cleared product, ensuring quality and reliability.
- Unique ECG measurement capability.
- WiFi and Bluetooth connectivity for smart features.
- AI-analyzed ECG results for cardiovascular health assessment.
- Reasonably priced compared to other models.
- Rechargeable via USB cable.
- Comes with a 1-year warranty.
- Available for purchase on the official website in four options.
CONS
- Challenges in warranty claims and returns in some regions.
- Some users have reported accuracy issues.
Try Checkme Today
SPECIAL OFFER: Use code EMTSPOT15 to get 15% OFF

4. QardioArm – Best for small and large arms
Features
- Wireless, portable, easy to use
- Accurate systolic and diastolic readings
- Irregular heartbeat detection
- Syncs with major health apps
- Shareable data via Email
Qardio, the company behind QardioArm, is renowned for its high-quality product design and is headquartered in San Francisco, CA, United States.
Qardio has built a reputation for its innovative health technology products, notably the QardioArm, a wireless blood pressure monitor that embodies the brand’s dedication to style, convenience, and accuracy.
This product serves as a smart, wireless blood pressure monitor, facilitating the effortless monitoring of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, in addition to an irregular heartbeat detection function.
Users particularly value its accuracy and user-friendliness, especially when used alongside its companion app, which provides valuable medical insights.
Clinically validated and 510(k) FDA-cleared, the device is capable of measuring a broad range of blood pressure and heart rates.
It seamlessly syncs with Apple Health, Samsung Health, or Google Fit, streamlining the recording and sharing of health data with healthcare providers.
The brand’s overall reputation for quality and design in health technology products further fosters trust and satisfaction among users of the QardioArm blood pressure monitor.
PROS
- Clinically validated and FDA cleared.
- Compatible with Apple Health, Samsung Health, and Google Fit.
- Data sharing capabilities with doctors.
- It is one of the lightest weight options available in the market.
- Stylish and convenient design.
- Three-year limited warranty.
- Available for purchase on the official Qardio store at a discounted price.
CONS
- Requires a smartphone for operation, which might not be convenient for all users.
Try QardioArm Today

5. Oxiline Pressure 9 Pro – Best for use during pregnancy
Features
- Accurate measurements
- Double accuracy check system
- Fully automatic operation
- Automatic recording
- Vibra T9 technology
The Oxiline Pressure 9 Pro, manufactured by Oxiline LLC, is a hallmark of blood pressure monitoring technology innovation.
Headquartered in the USA, Oxiline has established itself as a reputable company, consistently delivering devices that blend advanced technology with user-friendliness.
The Pressure 9 Pro, an upgraded version of the Pressure 7 Pro, exemplifies this blend. Its precise and reliable blood pressure readings stand out, underscoring the device’s effectiveness.
Users appreciate its ease of use and functionality, contributing to its positive crowd perception.
The inclusion of a lifetime warranty and a 30-day trial period further asserts the company’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, making the Pressure 9 Pro a technologically superior and user-centric blood pressure monitor.
PROS
- Compact and well-designed.
- One-button easy operation.
- Fast measurements.
- Feature-rich settings menu.
- Wide cuff range for all arm sizes.
- Smart alarm for low measurements.
- Highly accurate sensor.
- Quick readings.
- 5-inch LCD screen with high contrast.
- Consistently near-perfect readings.
- A lifetime warranty and various purchase options are available.
CONS
- Limited viewing angles.
- No continuous 24/7 monitoring.
- No app support.
SPECIAL OFFER – 10% OFF
This is for TheEMTSpot’s readers only! Use code: EMTSPOT10 at the checkout to get 10% DISCOUNT.

6. iHealth Track – Best for irregular heartbeat
Features
- Clinically validated accuracy
- Color-coded bp range indicator
- Simple, one-button operation
- Large, easy-to-read display
- iHealth my vitals app integration
iHealth, a pioneer in digital health from Silicon Valley, was founded in 2010 and quickly rose to prominence with the launch of the world’s first Bluetooth-connected blood pressure monitor compatible with iOS devices.
The company has consistently focused on integrating FDA 510K cleared, award-winning medical devices with a remote patient monitoring platform, thereby establishing a robust digital health ecosystem known as the Unified Care model.
This model has notably impacted chronic disease management, especially in hypertension and diabetes.
The iHealth Track Blood Pressure Monitor reflects this legacy, offering users a clinically validated and FDA-cleared solution for home blood pressure monitoring.
It’s known for its accuracy, ease of use, and effective integration with the iHealth My Vitals App, which adds to its functionality and appeal.
The device’s crowd perception is generally positive, with users appreciating its design, user-friendly interface, and reliable performance.
PROS
- Compact, user-friendly design.
- Precise blood pressure measurements.
- Easy-to-read, color-coded display.
- Intuitive setup and operation.
- Compatible with a free, comprehensive app.
- Provides a large adult cuff, with an XL option available.
- Offers a 1-year limited warranty.
CONS
- Lacks a protective carrying case.
- Unable to change the date without app pairing.
Try iHealth Track Today

7. Omron HEM 6161 – Best wrist monitor
Features
- Irregular heartbeat detector
- Cuff wrap detector
- Body movement indicator
- One-touch operation
- Memory for 30 readings
Omron, a Japanese brand, is renowned for its innovative approach to manufacturing self-monitoring medical devices, including blood pressure monitors.
The brand stands out for its precision and has gained global trust, making it a preferred choice among healthcare professionals.
The Omron HEM 6161, a wrist blood pressure monitor, exemplifies this reputation.
It uses the oscillometric method for blood pressure measurement, ensuring maximum accuracy, with a claimed accuracy of ±3 mmHg for blood pressure and ±5% for pulse rate.
The monitor is user-friendly and convenient for regular tracking, featuring a body movement indicator, cuff wrap detection, and an irregular heartbeat detector.
These attributes, along with its compact design, make it highly useful for users, especially those needing to monitor their blood pressure while traveling or at work.
Its ease of use and reliability have earned it a favorable acceptance among users, especially in the Western world.
PROS
- Detects irregular heartbeats.
- Indicates correct cuff wrapping.
- Signals body movement during measurement.
- Simple one-touch operation.
- Stores up to 30 readings.
- Compact and portable design.
- The package includes the monitor, case, batteries, warranty card, and user guide.
CONS
- Not suitable for diabetic patients.
- Cannot set a date or time.
- Lacks hypertension indicator.
Try Omron HEM 6161 Today

8. Withings BPM Connect – Best for Apple Health
Features
- FDA medically cleared
- Apple Health integration
- Portable and user-friendly
- Built-in rechargeable battery
- Matrix LED screen display
The Withings BPM Connect, a portable blood pressure monitor with Apple Health support, demonstrates Withings continued commitment to innovative health technology.
Withings, a company that has been integral in the development of health-related devices, integrates its products seamlessly with Apple’s health ecosystem.
The BPM Connect, being FDA-cleared, stands out for its functionality and ease of use. It offers medically accurate readings that are automatically integrated into Apple Health via the Withings Health Mate app.
This feature-rich device’s user-friendly design, including its integrated matrix LED screen and one-button operation, makes it convenient for users to monitor their blood pressure.
It’s highly regarded for its portability, making it an excellent choice for users who need to monitor their blood pressure while on the go.
The BPM Connect’s impressive features and reliability have garnered positive reviews and a strong reputation among users.
PROS
- Medically accurate blood pressure readings.
- Easily integrates with Apple Health and the Withings Health Mate app.
- Compact and portable design.
- Long battery life of up to 6 months.
- Recognizes multiple users and displays their names.
- The BPM Connect is available for purchase at various retailers, including Amazon and direct from Withings.
CONS
- Uses micro USB instead of USB-C for charging.
Try Withings BPM Connect Today

9. Omron Evolv – Best for Samsung Health App
Features
- Wireless Bluetooth connectivity
- Irregular heartbeat detector
- Compact one-piece design
- Omron CONNECT app integration
- Compatible with Samsung Health
Omron, a leading name in health monitoring devices, presents the Omron Evolv, a wireless blood pressure monitor that seamlessly syncs with smartphone apps through Bluetooth.
This device is part of Omron’s innovative approach to health technology, offering users a convenient way to monitor blood pressure without dealing with twisted tubes or wires.
The Evolv is known for its sleek design and ease of use, facilitating regular blood pressure readings at home. It effectively integrates with both iPhone and Android devices, including compatibility with the Samsung Health app.
This connectivity allows for easy tracking of blood pressure fluctuations and sharing of results with healthcare providers.
The Omron Evolv’s functionality and user-friendliness have earned it positive feedback, making it a well-regarded tool for personal health management.
PROS
- Sleek and portable.
- Easy to use with intuitive controls.
- Stores unlimited readings via the Omron Connect app.
- Monitors blood pressure trends and shares results.
- Comes with a 5-year warranty.
- Available for purchase from various retailers, including Amazon.
CONS
- Reported bugs in pairing and syncing
Try Omron Evolv Today
How to take blood pressure at home?
To take blood pressure at home, it’s important to adhere to certain guidelines, especially those recommended by the American Heart Association (AHA).
According to AHA, blood pressure can vary throughout the day, so it’s recommended to check it either in the morning upon waking up or in the evening before going to bed.
This timing can yield more consistent readings and is acceptable whether done before or after taking blood pressure medication.
Professor Barry P. McGrath, an Adjunct Professor of Medicine at Monash University, suggests conducting blood pressure measurements both in the morning and evening for at least five consecutive days to accurately diagnose hypertension or any other variations in blood pressure.
Proper preparation is crucial, involving emptying the bladder and allowing at least five minutes of relaxation before measurement.
Sit with a straight, well-supported back, feet flat on the floor, and legs uncrossed. Ensure that the arm wearing the cuff is exposed, positioned at heart level and that the cuff’s lower edge aligns with the elbow bend.
During this preparation phase, it’s important to relax, avoid conversation, and eliminate distractions such as cell phones.
Using a blood pressure monitor follows several key steps as recommended by the AHA.
- Start the process by sitting in a chair with both feet flat on the ground and maintaining a straight back, resting for approximately five minutes before measuring.
- Next, place your arm on a surface at heart or chest level, follow your machine’s instructions, and remain still and silent throughout the process.
- For enhanced accuracy, consider taking a second reading 1 to 2 minutes later and calculate the average of the two readings.
The above steps are critical in ensuring accuracy, but despite that, you may get false readings from your device. The next section will help you understand how.
Can home blood pressure monitors give false readings?
Yes, your home blood pressure monitor may provide a false reading, similar to a clinical one. The significant difference is that a clinician might be able to identify it, while you may not.
Dr. Swapnil Hiremath, a kidney specialist at Ottawa Hospital, highlights that the accuracy of home blood pressure monitors can vary, stating that:
“Home blood pressure monitors may be inaccurate in 5% to 15% of patients, depending on the threshold for accuracy used.”
This inaccuracy can lead to incorrect medication adjustments, emphasizing the importance of selecting a reliable device.
Dr. Christian Ruff, a cardiologist at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women’s Hospital, points out that blood pressure measurements can vary even when taken using precise methods.
To enhance accuracy, he recommends taking multiple recordings and averaging them for a more reliable assessment of your blood pressure.
One significant issue is that many home blood pressure monitors on the market are not validated for accuracy.
A study reported in JAMA found that a substantial percentage of upper arm cuff and wrist cuff monitors sold on Amazon.com were not validated, which poses a risk to health. Inaccurate measurements could lead to unnecessary doctor visits or incorrect medication adjustments.
The absence of a global institution for standardizing blood pressure monitor validation complicates matters.
However, organizations like the American Medical Association and STRIDE BP have compiled lists of validated devices. It’s crucial to select a monitor that has undergone validation to ensure accurate readings.
Additionally, the accuracy of a blood pressure monitor can depend on factors such as cuff size and device features.
Dr. Christopher Cannon, a cardiologist and editor in chief of the Harvard Heart Letter, stresses the importance of using a well-fitting cuff.
He also recommends devices with a large, easy-to-read display and an automatically inflating arm cuff to enhance accuracy and user-friendliness.
Should your blood pressure readings be the same on both arms?
No, blood pressure readings are not always the same on both arms. It’s quite common for there to be a slight difference in blood pressure readings between the two arms.
This difference can be attributed to various factors, such as differences in arm size, blood vessel conditions, or even the positioning of the cuff during measurement.
As stated by Dr. Tim from Mercy Medical Center:
“Researchers have found [that] the difference between the top numbers in your arms can predict your risk for heart and vascular disease.”
This emphasizes the importance of checking blood pressure in both arms. He further revealed that in a study, “the average [difference] was about 3 to 5 millimeters,” which is the top number or systolic blood pressure.
Notably, “10% of the patients had a [difference of] 10 millimeters or greater.” Such differences are crucial as “those patients, when followed [were at a] risk for developing coronary heart disease.”
This information underscores the necessity of monitoring blood pressure in both arms for a more comprehensive assessment of cardiovascular risk.
However, significant differences in blood pressure readings between the two arms can be indicative of underlying health issues.
One such condition is atrial fibrillation (AFib). But should you continue using a blood pressure monitor in that case?
Can you use a blood pressure monitor while having atrial fibrillation?
Using a blood pressure monitor with atrial fibrillation (AFib) can present challenges. AFib is characterized by an irregular and often rapid heartbeat, which can potentially impact the accuracy of blood pressure measurements.
Researchers from Exeter College of Medicine and Health, as reported in a Nature article, suggest that for patients with AFib, manual blood pressure monitors should be considered over automatic ones.
Many standard blood pressure monitors are optimized for regular heartbeats and may not provide accurate readings for individuals with AFib.
Fortunately, there are newer models of blood pressure monitors specifically designed to provide more accurate measurements for people with irregular heart rhythms like AFib.
These advanced monitors utilize algorithms to account for pulse rate and rhythm variability, enhancing the reliability of readings.
If you have AFib and need to monitor your blood pressure, consider the following steps.
- Consult with your doctor: Seek your healthcare provider’s guidance to recommend a blood pressure monitor suitable for irregular heart rhythms.
- Look for AFib-specific monitors: Some devices are designed to be more accurate for individuals with AFib and may be labeled as suitable for use with irregular heartbeats.
- Validate accuracy: Ensure that the chosen monitor has been clinically validated for precision, especially for AFib patients.
- Follow proper technique: Accurate readings depend on correct positioning and relaxation during measurements. Adhere to the provided instructions diligently.
- Compare with clinical readings: To verify accuracy, it can be beneficial to compare home monitor readings with those obtained during medical appointments.
Home monitoring can assist in managing your health. It should complement, not replace, regular medical consultations, especially for conditions like AFib.
While monitoring blood pressure with AFib can be challenging, what about individuals with pacemakers? Are blood pressure monitors safe for them?
Can you use a blood pressure monitor with a pacemaker?
Using a blood pressure monitor alongside a pacemaker is generally regarded as safe, especially when employing an upper-arm blood pressure monitor.
However, it is recommended to avoid wrist blood pressure monitors, as the cuff may interfere with the pacemaker’s function.
According to the AHA, consumer appliances and electronics, including blood pressure monitors, typically do not affect the performance of pacemakers or ICDs (implantable cardioverter defibrillators).
On rare occasions, some devices may briefly interrupt pacemakers, but they quickly restore normal signals. Keeping all motors and antennae at least six inches from your pacemaker is important.
Individuals with pacemakers should regularly check their blood pressure for their well-being.
When using a blood pressure monitor, it is vital to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cuff placement on the upper arm and ensure it is at least six inches away from the pacemaker.
Additionally, seeking guidance from your doctor regarding the type and model of blood pressure monitor to use with a pacemaker is advisable.
They can provide personalized recommendations and advice tailored to your individual health requirements.
While pacemakers may not be affected by your monitor, you may wonder if you can use your blood pressure monitor on your forearms. Learn about this in the next section.
Can you use a blood pressure cuff on the forearm?
While it’s possible to use a blood pressure monitor on the forearm to obtain a measurement, it’s generally recommended to use it on the upper arm for more accurate readings.
Most blood pressure monitors are designed for use on the upper arm because they tend to provide more consistent and reliable results.
Using the forearm for measurements may yield less accurate results and may not be suitable for all types of blood pressure monitors.
However, it’s important to note that a study published in the Journal of Hypertension, titled “Forearm Compared To Upper Arm Blood Pressure Readings,” found significant differences between forearm and upper-arm blood pressure measurements.
This study revealed that systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings were notably lower when measured on the upper arm compared to the forearm.
Specifically, the mean systolic and diastolic blood pressures on the forearm were 142.7 ± 16.5 mmHg and 86.8 ± 13.4 mmHg, respectively, while on the upper arm, they were 122.3 ± 16.6 mmHg and 72.8 ± 11.6 mmHg, respectively.
This significant difference suggests a potential need for establishing forearm blood pressure reference values, particularly for individuals with larger arms, where upper-arm measurements might not be as accurate.
If you’re considering using your blood pressure monitor on the forearm, it’s advisable to consult your doctor beforehand to ensure the monitor’s accuracy in that position.
Moreover, understanding how to choose the right monitor, as explained in the next section, can be beneficial for you.
How to choose a blood pressure monitor?
Having the right blood pressure monitor is a crucial step because, no matter how informed you are about how to measure, not having the right tool may sabotage the reading.
According to British Heart Foundation guidelines, the following suggestions might help you make the right choice.
- Ask your doctor: It’s essential to consult your healthcare provider when selecting a blood pressure monitor. They can recommend a suitable model based on your specific health needs, ensuring that it aligns with your treatment plan and medical condition.
- Buy a monitor with an upper cuff: Upper arm cuffs provide more accurate and consistent readings than wrist or finger monitors. Opting for an upper arm monitor is generally recommended for reliable results.
- Make sure the cuff is right for your arm: Choose a monitor with a cuff that fits your arm comfortably and snugly. An ill-fitting cuff can lead to inaccurate readings. Most monitors offer different cuff sizes, so ensure you select the appropriate one for your arm size.
- Consider cost: Blood pressure monitors come in a range of prices. Consider your budget while selecting a monitor, and prioritize accuracy and reliability. Sometimes, investing a bit more in a quality monitor can benefit your long-term health management.
- Choose one that’s easy to use: Opt for a monitor with a user-friendly design and clear instructions. A simple interface and intuitive operation can make monitoring your blood pressure at home much more convenient.
- Select your desired features: Different monitors offer Bluetooth connectivity, data storage, or irregular heartbeat detection. Choose a monitor with features that align with your health goals and preferences.
- Read customer reviews: Customer reviews and ratings can provide valuable insights into the performance and reliability of a blood pressure monitor. Consider the experiences of other users when making your decision.
- Check for a warranty: It’s a good practice to ensure the monitor has a warranty. A warranty can provide peace of mind in case the monitor encounters any issues or malfunctions.
- Make sure you get it serviced every 2 years: Regular maintenance and servicing of your blood pressure monitor are essential to ensure its accuracy and longevity. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance, including calibration or servicing every two years, can help maintain its reliability.
These elaborations should give you a clearer understanding of the importance and considerations for each point when choosing a blood pressure monitor.
The type of monitor alone could be the topic of a study, and that’s why the below section is dedicated to the same.
Which type of blood pressure monitor is the most accurate?
To achieve the most dependable blood pressure measurement, the AHA suggests utilizing a home blood pressure monitor equipped with an upper arm cuff.
This recommendation is based on the higher accuracy and consistency of upper arm monitors compared to other types of blood pressure measuring devices.
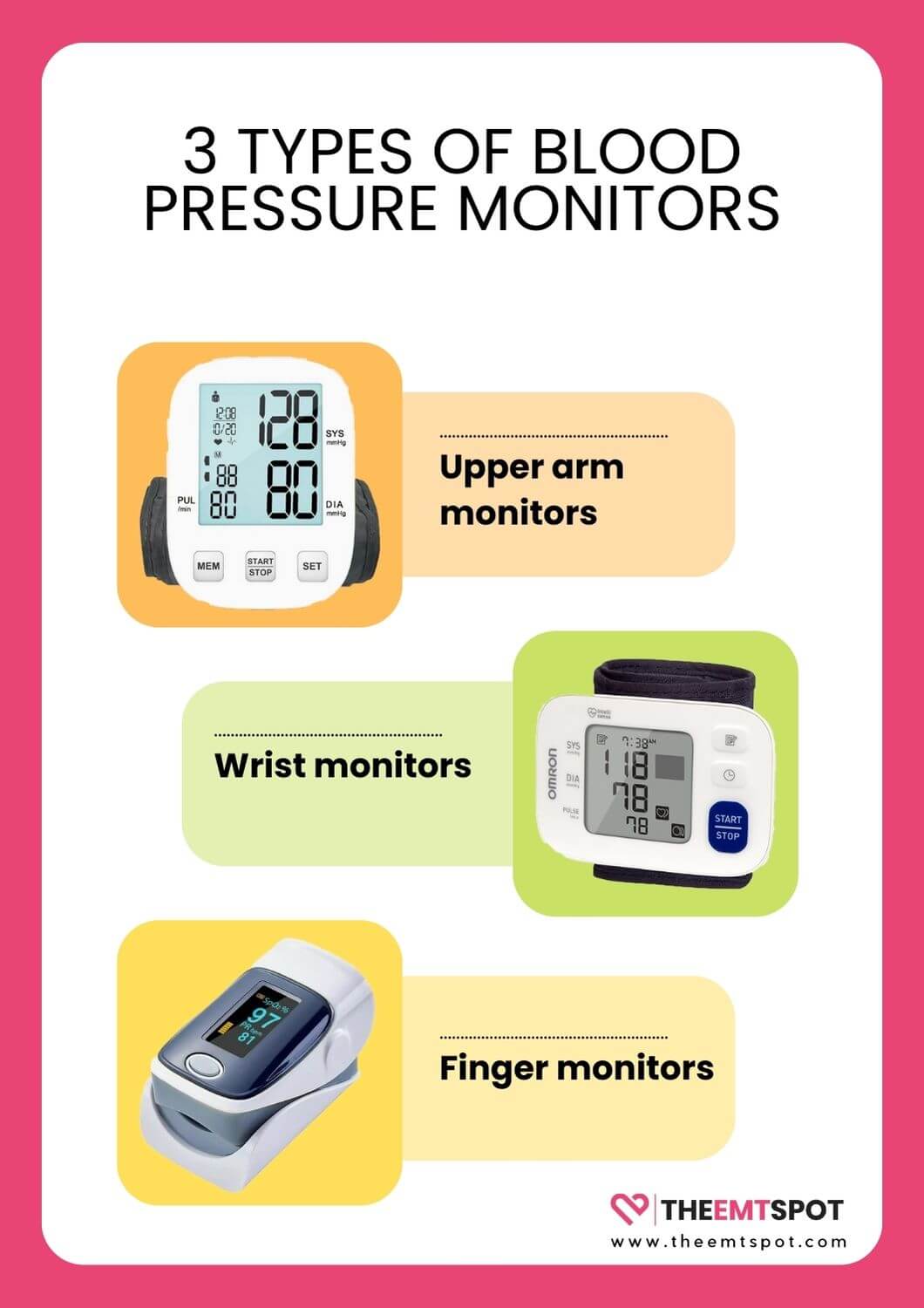
Upper arm monitors
Upper-arm monitors are preferred because they measure blood pressure at the level of the heart, providing more accurate and consistent readings.
The brachial artery in the upper arm is closer to the heart level, which helps obtain readings more reflective of central blood pressure.
Wrist monitors
Wrist monitors, though increasing in popularity and improving in accuracy, are generally considered less reliable than upper-arm monitors.
This is partly due to the narrow vessels in the wrist and difficulty correctly positioning the monitor.
Dr. Don Pham, a cardiologist, points out, “In general, wrist monitors are more likely to report higher readings due to the narrow vessels in the area and difficulties in positioning correctly.”
A study from Tohoku University published in the Journal of Hypertension analyzed wrist monitors and found that, although they are becoming more accurate, proper placement and setup are crucial for obtaining accurate readings.
This study showed that wrist monitors had a mean difference of -2.1/-2.3 mmHg for systolic blood pressure and 1.2/-5.6 mmHg for diastolic blood pressure when compared with standard auscultation.
The variability in readings, especially in different wrist positions, indicates that these devices may not be suitable for self-measurement of blood pressure for general, clinical, or practical use.
Finger monitors
Finger blood pressure monitors, often marketed to consumers as accurate devices, have been found to have no statistically significant correlation with standard cuff measurements.
A study published in the journal Family Medicine by J. M. Nesselroad et al. tested three models of automated finger blood pressure devices against standard cuff measurements and found considerable inaccuracies.
This study concluded that patients should be cautious about relying on these devices for accurate blood pressure measurements.
In summary, while wrist and finger monitors offer convenience and are evolving in terms of technology and accuracy, they currently do not match the reliability of upper-arm monitors.
The AHA and other medical professionals recommend upper arm monitors for their proven accuracy and consistency in blood pressure measurements.
For individuals who cannot use upper arm monitors, such as those with very large arms or those who have had axillary lymph node resection, wrist monitors can be used with careful attention to positioning and setup.
While the type of monitor is essential, many users overlook another crucial aspect, which is the cuff size. The next section will help you understand that.
Does the cuff size of a blood pressure monitor matter?
The size of the cuff plays a pivotal role in achieving precise blood pressure measurements, and sometimes, it could be a difference between life and death.
According to Anika L. Hines, Ph.D., MPH, an assistant professor of health behavior and policy at the Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine, “using a measuring tape in clinical practice seems less practical.”
While the practicality of using a measuring tape in clinical practice may be limited, it remains crucial to ensure accurate readings.
Furthermore, Junichi Ishigami, MD, PhD, an assistant scientist of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, stated, “An overestimation of blood pressure could potentially result in overtreatment of hypertension, leading to unnecessary adverse effects from medical interventions and increased expenditure on medications.”
Recent research, as reported in a 2023 study published in JAMA Internal Medicine, highlights the ramifications of using the wrong cuff size during blood pressure measurement.
When the cuff is too small, it may yield artificially elevated blood pressure readings, while an excessively large cuff can produce falsely low measurements.
The pivotal message is that selecting the appropriate cuff size for a blood pressure monitor is indispensable for obtaining precise readings.
The cuff should comfortably encircle around 80% of the upper arm, stretching from the elbow to the armpit.
Cuff sizes are typically categorized as small, regular, large, or extra-large, with specific centimeter measurements provided.
Ensuring the correct cuff size is fundamental to securing accurate and reliable blood pressure measurements.
Where to buy a blood pressure monitor?
When it comes to monitoring your blood pressure at home, having the right equipment is essential.
Choosing the right blood pressure monitor begins with knowing where to buy one and understanding what to look for to make an informed purchase.
- Retail stores: You can find blood pressure monitors at various retail locations such as pharmacies, supermarkets, and big-box stores. Retail stores offer the advantage of seeing the product in person before making a purchase. You can also get assistance from store staff to help you choose the right monitor.
- Online retailers: Online shopping has become increasingly popular for purchasing healthcare equipment, including blood pressure monitors. Websites like Amazon, Walmart, and medical supply stores offer a wide range of options. Reading customer reviews and comparing prices can be helpful when buying online.
- Medical supply stores: Specialty medical supply stores often carry a selection of high-quality blood pressure monitors. They can provide expert guidance and recommendations based on your specific needs.
When planning to make a purchase, keep the following points in mind to ensure a smart purchase.
- Customer support and service: Good customer service, including helpful advice on choosing and using the monitor, is important. Also, check the availability of after-sale support and warranty services.
- Reputation and reliability: Opt for reputable sellers or medical supply stores known for quality products. Check customer reviews and ratings.
- Price comparison: Compare prices among different sellers to ensure you are getting a fair deal. Be cautious of prices that seem too low, as they might indicate a counterfeit or substandard product.
- Healthcare provider recommendations: Sometimes, healthcare providers can recommend places known for quality medical supplies.
- Additional services: Some stores offer additional services like blood pressure monitoring tutorials or in-store health checks.
- Privacy and security: If buying online, ensure the website is secure and respects your privacy, especially if you are providing medical information.
- Range of products: Whether it’s online or offline, select a source offering a variety of models, so you have options to compare features, brands, and prices.
While the above suggestions will help you make an informed decision, also consider checking with friends and family for recommendations, which can often be the best choice.
If you’re wondering about price comparisons among different types, check out the next section.
How much do blood pressure monitors cost?
The cost of blood pressure monitors varies widely, generally ranging from $20 to over $100.
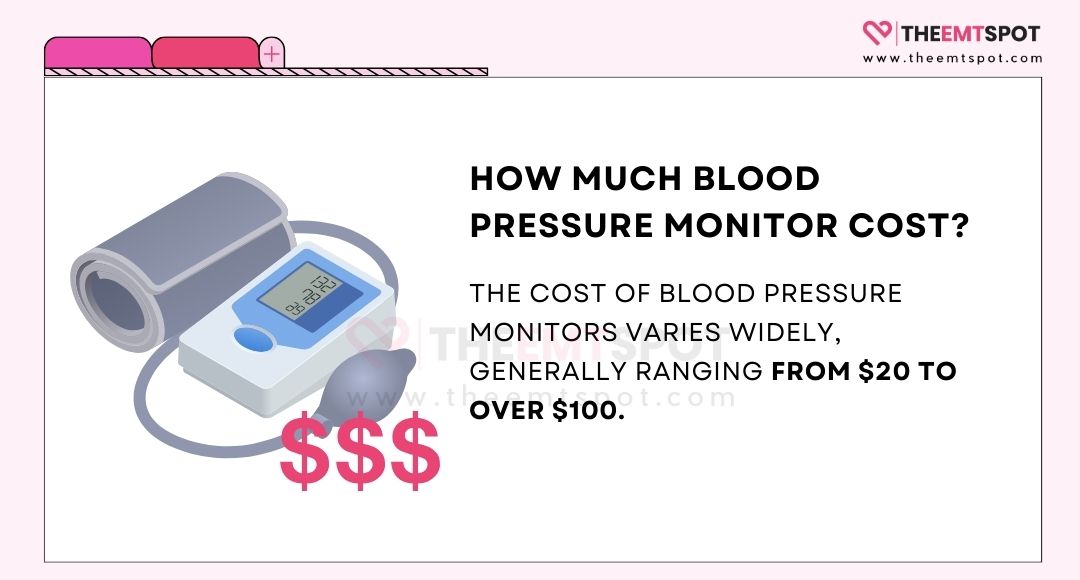
This price variation reflects differences in features, brand, accuracy, and additional functionalities. Some examples are given below.
- Omron Series 10 ($70): Known for its accuracy and reliability.
- Oxiline Pressure X Pro ($119): Offers smart connectivity at a moderate price.
- CheckMe BP2A ($99): A budget-friendly smart monitor.
Cheap vs expensive monitors: The primary differences between cheaper and more expensive blood pressure monitors lie in accuracy, durability, extra features like Bluetooth connectivity, data tracking, multiple user capabilities, and comfort. Higher-priced models often undergo more rigorous testing and validation.
Buying a cheap monitor: Purchasing a cheaper blood pressure monitor can be worthwhile if your needs are basic. For occasional monitoring and for users without complex health issues, an affordable monitor can be a practical choice.
Investing in an expensive monitor: Expensive blood pressure monitors are generally more accurate and durable. They are advisable for individuals with serious health conditions, like hypertension, who require precise monitoring. The added features, like data syncing with health apps, are beneficial for long-term health tracking.
Choosing the right monitor
- Opt for a cheaper model when:
- Budget is a constraint.
- You need it for occasional, basic monitoring.
- There are no serious underlying health issues.
- Choose an expensive model when:
- Accuracy is critical.
- You have a medical condition that requires continuous monitoring.
- You prefer advanced features for ease of use and data tracking.
Taking into account the factors mentioned above will assist you in choosing a blood pressure monitor that suits your healthcare requirements and financial constraints.
But did you know that some insurance companies may cover the cost of a blood pressure monitor? Read on to learn more below.
Does insurance cover a blood pressure monitor?
Certainly, insurance coverage for blood pressure monitors can be available, but it varies depending on your individual insurance plan and the insurance company providing the coverage.
Some insurance plans may cover the cost of a blood pressure monitor if it’s prescribed by a physician or if it’s deemed medically necessary.
Examples of Insurance companies offering coverage for blood pressure monitors and similar devices are given below.
- United Healthcare: They cover at least some of the cost of a blood pressure monitor, especially if prescribed by a doctor.
- Blue Cross Blue Shield: This insurance provider covers blood pressure monitors when prescribed by a physician.
While this may not be included in your regular package, there is always a choice for the insurer to get it as an add-on. Some of the other things you should know are added below.
- Medicare coverage: Medicare generally does not cover blood pressure monitors for home use, except under specific circumstances, such as if you’re receiving dialysis treatments at home or if your doctor orders ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
- Cost of insurance: The cost of insurance that covers blood pressure monitors varies depending on the plan and the insurer. It is recommended that you get in touch with your insurance company for accurate details regarding expenses and insurance coverage.
- Conditions for coverage: Coverage typically requires a prescription from a healthcare provider and may depend on whether the monitor is deemed medically necessary.
It is advisable to contact your insurance provider directly to comprehend the specific terms and conditions of blood pressure monitor coverage.
How do you read a blood pressure monitor?
Reading a blood pressure monitor involves understanding some fundamental principles. The below points will help you correctly measure your blood pressure.
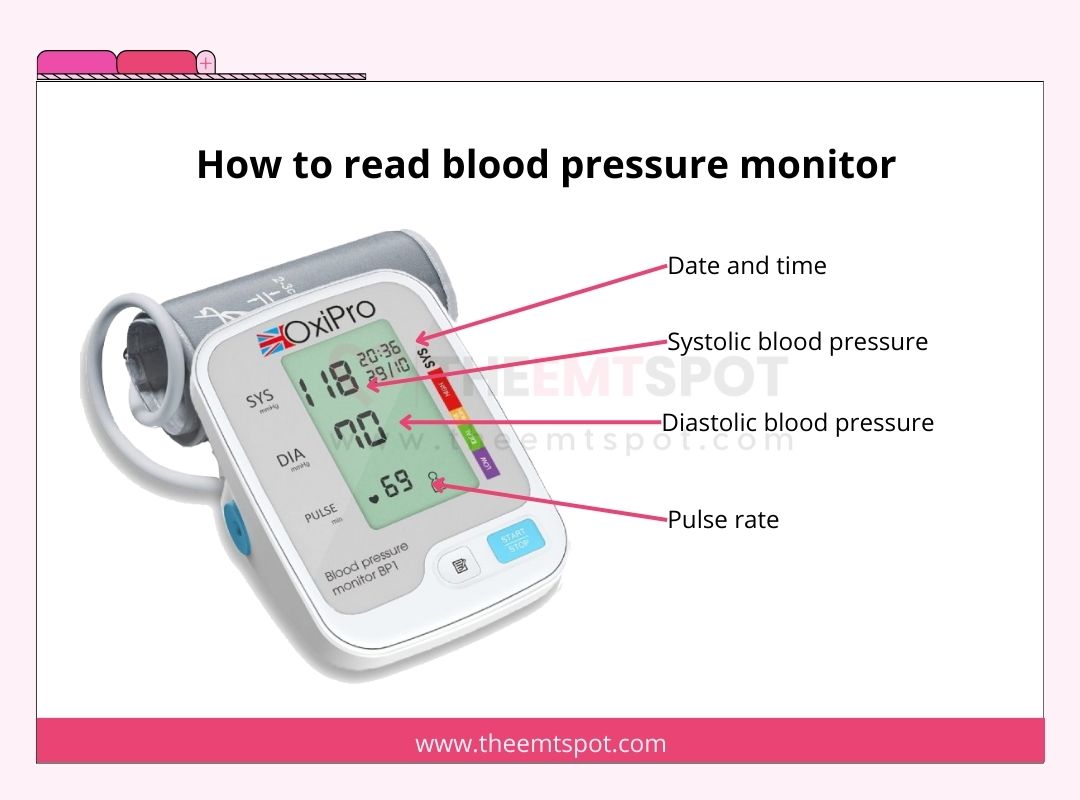
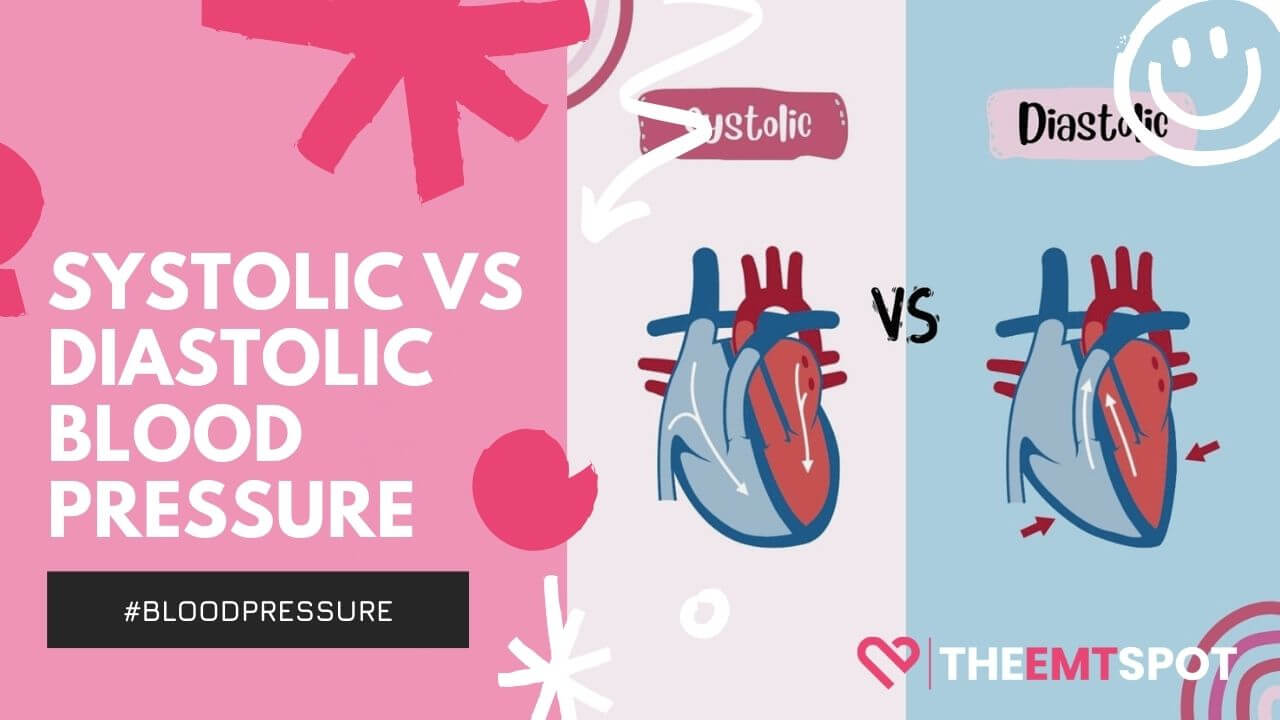
- Comprehending blood pressure readings: Blood pressure readings consist of two numbers, typically presented as systolic over diastolic:
- Systolic pressure (top number): This represents the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats. A normal systolic pressure should be below 120 mmHg.
- Diastolic pressure (bottom number): This indicates the pressure in your arteries between heartbeats. A normal diastolic pressure should be below 80 mmHg.
- Reading the display: Most digital blood pressure monitors display the systolic pressure above the diastolic pressure. For example, when the reading shows 120/80 mmHg, it means the systolic pressure is 120 mmHg, and the diastolic pressure is 80 mmHg.
- Interpreting the results: According to guidelines from the AHA, Harvard Health, and the CDC, blood pressure health is categorized into the following stages: normal, elevated, stage 1 and stage 2 hypertension, & hypertensive crisis, as elaborated in detail in the next section.
- Considering consistency: A single reading isn’t sufficient for a comprehensive assessment. It’s essential to monitor your blood pressure consistently over time and consult healthcare professionals for accurate interpretation and guidance.
What are the stages of blood pressure regarding AHA’s blood pressure chart?
According to the AHA guidelines for cardiovascular care, blood pressure health is gauged based on the following baselines. To learn more about blood pressure chart, click here.
STAGE (Clinical Term) | SYSTOLIC mm Hg [upper #] | DIASTOLIC mm Hg [lower #] | |
NORMAL BP | Less than 120 | and | Less than 80 |
PRE-HYPERTENSION (Elevated Blood Pressure) | 120-129 | and | Less than 80 |
HIGH BP (Hypertension STAGE 1) | 130-139 | or | 80-89 |
HIGH BP (Hypertension STAGE 2) | 140-180 | or | 90-120 |
VERY HIGH BP (Hypertensie Crisis) | Higher than 180 | and/ or | Higher than 120 |
Non-standard references
- Hypotension: 80/50 – 90/60 mmHg
- Severe hypotension: Below 80/50 mmHg
Hypotension is usually not treated as a medical emergency unless the patient has a pre-existing disease related to it and is unconscious.
Unlike hypertension, hypotension doesn’t cause any medical threat in most cases. AHA’s primary concern is addressing and preventing cardiovascular diseases, which are more commonly associated with elevated blood pressure levels.
More in this topic






 Robin Backlund is a dedicated journalist and a medical student who has written several articles and essays exposing the falseness and hollowness of online resources in the medical science niche.
Robin Backlund is a dedicated journalist and a medical student who has written several articles and essays exposing the falseness and hollowness of online resources in the medical science niche.